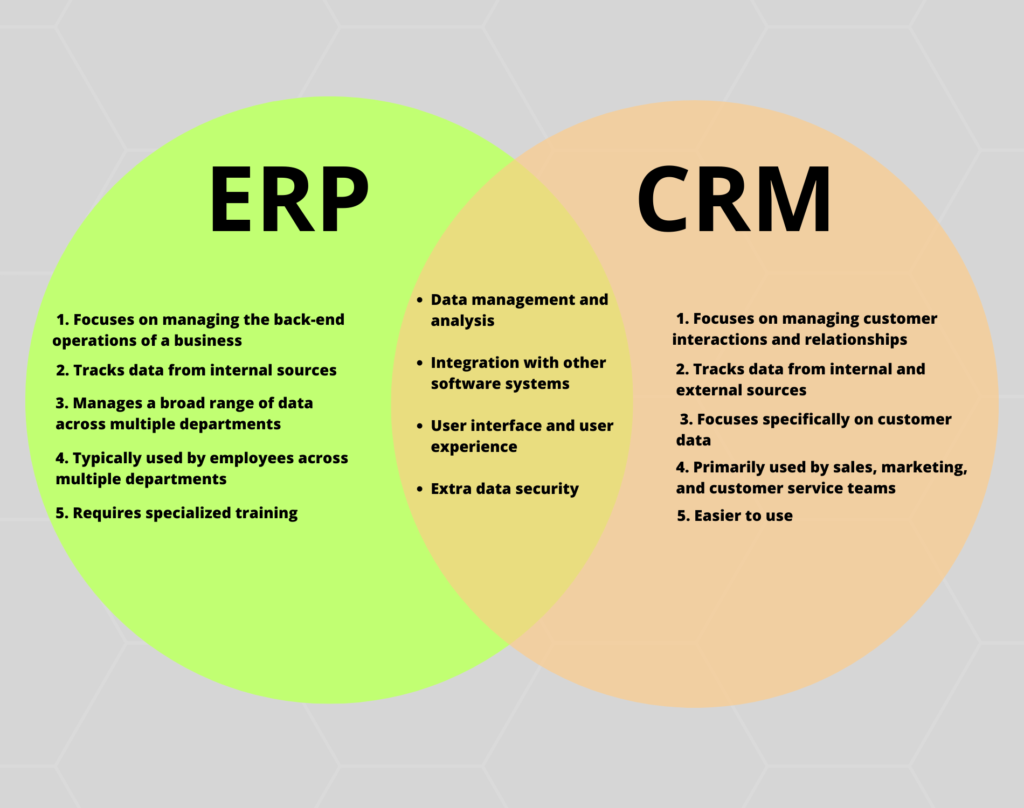
As businesses grow and evolve, organizing and managing their business operations become increasingly complex. ERP and CRM systems provide solutions to this problem, providing valuable insights and streamlining essential functions. However, they are not one and the same thing.
While ERP systems manage internal business processes, CRM systems focus on managing sales pipelines, customer interactions and satisfaction. In this blog, we’ll be taking a closer look at ERP and Customer Relationship Management systems, clearing up the confusion that often surrounds them. We’ll explain the differences between ERP and CRM and how they can help businesses manage their operations and thrive.
What Is ERP and CRM?
ERP software is an integrated suite of applications designed to automate and streamline essential business functions such as finance, accounting, inventory management, procurement, and human resources. By consolidating these functions into a single, unified system, ERP software enables businesses to optimize their operations, improve productivity, and reduce inefficiencies.
According to Aberdeen Group, 95% of companies saw an improvement in their business processes after implementing an ERP system. Moreover, advanced analytics capabilities often come with ERP systems to provide valuable insights into business performance, empowering data-driven decisions that drive growth and success.
CRM: Understanding the Customer is KeyWhile ERP software consolidates essential business functions to optimize internal operations, CRM software is a tool designed to help businesses manage and improve their customer relationships. Forrester-Freshworks research shows that 4 out of 10 firms boost revenues by 11-20% with a CRM implementation. In fact, 89% of companies see a revenue bump after implementing a CRM.
One of the defining characteristics of customer relationship management is its ability to streamline sales, marketing, and customer service operations. By consolidating customer data and automating tasks related to customer engagement, CRM software enables businesses to track customer interactions, analyze customer behavior, and personalize customer communications.
ERP vs CRM: What are the similarities?
Before we dive into the differences, it’s important that we get similarities out of the way. Understanding the similarities can help business owners choose the right system(s) for their needs and optimize their operations.
Data management and analysis
- Both ERP and CRM systems involve the management and analysis of business data to improve decision-making and optimize operations.
- While ERP systems primarily focus on managing and integrating data across various departments and functions, CRM systems focus on managing and analyzing customer data to improve customer interactions and satisfaction.
- Both systems provide advanced analytics capabilities that allow businesses to generate insights from their data and make data-driven decisions.
Integration with other software systems
- ERP and CRM systems can be integrated with other software applications to create a more efficient and effective business infrastructure.
- While ERP integration typically focuses on optimizing internal operations and creating a unified view of the entire business process, CRM integration is more focused on improving the customer experience and streamlining sales and marketing processes.
- Integration with other software systems can help businesses achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and productivity, as well as enhance their reporting and analysis capabilities.
User interface and user experience
- Both ERP and CRM systems strive to provide users with a seamless and intuitive interface that is easy to use and navigate.
- While ERP systems tend to have a more complex interface due to the broad range of functions they manage, CRM systems typically have a simpler and more streamlined interface that focuses on customer interactions and sales processes.
- Both systems strive to provide a positive user experience that meets the needs of their respective users.
ERP vs CRM: Where Do They Differ?
Primary Function
While both CRM and ERP systems are designed to help businesses manage their operations, they serve different primary functions. For comparison ERP software focuses on managing the back-end operations of a business, such as finance, accounting, and inventory management, while CRM software focuses on managing customer interactions and relationships.
Data Sources and Management
The difference between CRM and ERP systems when it comes to data, is that ERP software typically tracks data from internal sources, such as financial data and inventory levels, while CRM software tracks data from both internal and external sources, such as customer interactions on social media and website activity.
Furthermore, ERP software typically manages a broad range of data across multiple departments, while CRM software focuses specifically on customer data. ERP software is designed to provide a holistic view of a business’s operations, while CRM software provides a comprehensive view of customer interactions.
Users and Accessibility
ERP software is typically used by employees across multiple departments, such as finance, accounting, and human resources, while CRM software is primarily used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams. ERP software requires specialized training, while CRM software is typically easier to use.
Integration
When it comes to business operations, CRM and ERP integration plays a crucial role in streamlining processes and improving customer interactions. The integration of ERP and CRM systems with other software applications highlights a clear distinction between their respective purposes. ERP systems, designed to streamline business processes across various departments, focus on optimizing internal operations when integrated with other applications. This connectivity fosters increased efficiency, more accurate data sharing, and improved decision-making across the organization.
Conversely, CRM systems are dedicated to enhancing customer relationships by improving interactions and personalizing experiences. The integration of CRM systems with other applications aims to streamline sales and marketing efforts, provide valuable insights on customer behavior, and promote targeted engagement strategies. By incorporating CRM and ERP integration into their operations, businesses can achieve a more comprehensive view of their organization and customers, ultimately leading to improved performance, enhanced customer satisfaction, and sustained growth.
Who needs ERP software?
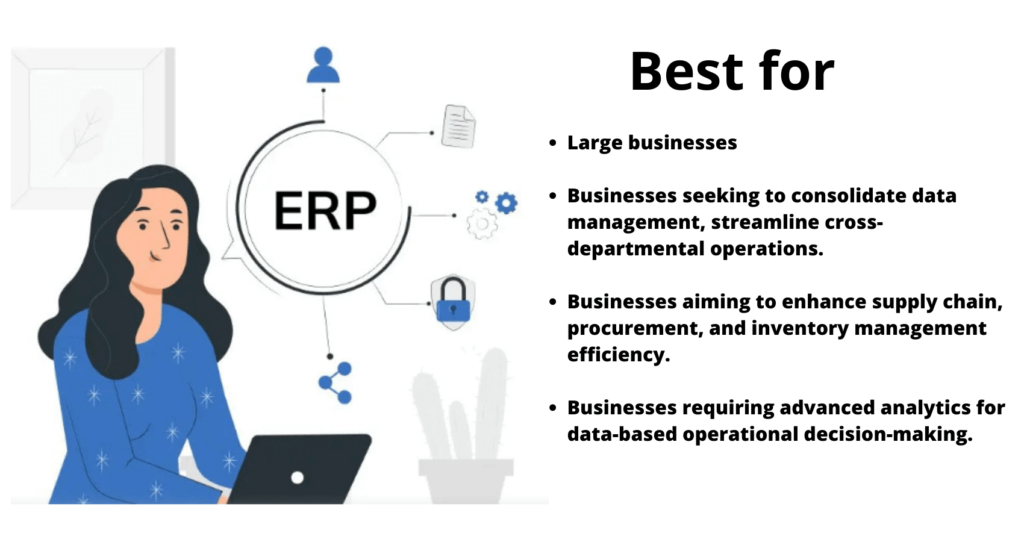
- Large businesses with complex operations that require management of multiple departments and functions, such as finance, accounting, procurement, inventory management, and human resources.
- Businesses that need to integrate and streamline their data management across multiple departments.
- Businesses that want to optimize their supply chain management, procurement, and inventory management processes.
- Businesses that need advanced analytics capabilities to make data-driven decisions about their operations.
For example, manufacturing companies that have multiple production lines, warehouses, and distribution centers may need ERP software to manage inventory, procurement, and logistics. Similarly, healthcare providers that have multiple clinics, departments, and locations may need ERP software to manage patient data, finances, and human resources.
While ERP software offers comprehensive data management across multiple departments, it may not be necessary for small or medium-sized businesses that have simpler operations. Additionally, some businesses may not need all the functionalities that ERP software offers.
Who needs CRM software?
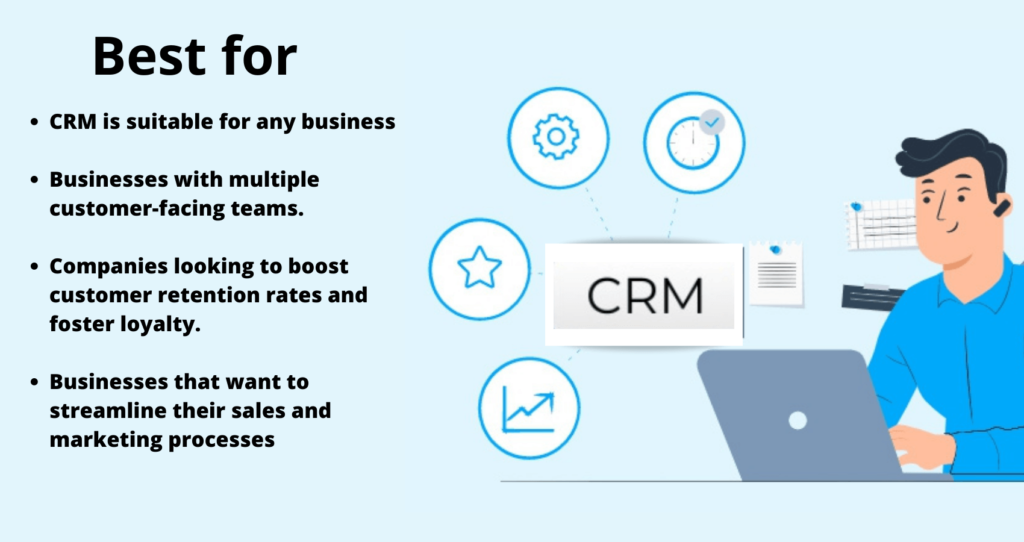
In today’s competitive business environment, virtually any business can benefit from CRM software. As businesses grow and expand their customer base, managing interactions and maintaining strong relationships becomes essential for success.
Businesses with multiple customer-facing teams, such as sales, marketing, and customer service departments, require efficient collaboration and a unified view of customer data to optimize their interactions and deliver a seamless experience.
Organizations that are data-driven and aim to leverage customer insights for informed decision-making can use CRM software to track and analyze customer data, enabling them to fine-tune their sales and marketing strategies.
Companies looking to boost customer retention rates and foster loyalty can benefit from CRM systems, which allow them to tailor personalized experiences and track customer preferences, leading to higher satisfaction and long-term relationships.
CRM software is also essential for businesses that want to streamline their sales and marketing processes by automating tasks, improving lead management, and integrating with other tools to create a cohesive and efficient system.
By adopting CRM software, organizations can stay ahead of the curve, ensuring they maintain a strong customer focus while improving internal collaboration and leveraging valuable insights for growth.
For instance, e-commerce businesses that want to provide personalized product recommendations and promotions to their customers may need CRM software to track customer behavior and preferences. Similarly, financial services companies that want to provide tailored investment advice and portfolio management to their clients may need CRM software to track client profiles and transactions.
While CRM software is essential for businesses that want to improve customer interactions and satisfaction, it may not be necessary for businesses that do not interact directly with customers. For instance, B2B businesses may not need CRM software as their sales cycles are often longer and require a different approach.
Who needs both CRM and ERP software?
Mid-sized and large businesses that require both comprehensive data management across multiple departments and a focus on improving customer interactions and satisfaction can benefit from CRM integration with ERP
Businesses that need to integrate and streamline their sales, marketing, and customer service processes with their internal operations.
Businesses that want to optimize their operations and improve their customer engagement and retention rates will also benefit from integrating ERP with CRM.
For example, a retail chain that wants to provide personalized shopping experiences to its customers may need both ERP and CRM software to manage inventory, logistics, and customer data. Similarly, a telecom provider that wants to offer customized service plans and billing to its customers may need both ERP and CRM software to manage network infrastructure, finances, and customer data.
The Winning Combo: SMP’s Sales Triumph with Zoho CRM and Oracle ERP Integration
SMP – Specialty Metal Products, a family-owned custom metal cutting and distribution business, faced a significant challenge due to the limitations of their ERP system, SM3 (Steel Manager III). While SM3 helped streamline their business processes, it was not a customer-centric system and could not provide insights into customer-level analysis, which hindered their growth. To address this issue, SMP realized they needed to adopt a CRM system, ultimately choosing Zoho One for its customization flexibility, commercial effectiveness, and mass marketing functionality. However, integrating their Oracle ERP database with Zoho CRM posed concerns regarding effort, time, and cost.
To overcome this challenge, SMP enlisted the help of Customerization , a digital transformation consultancy and provides CRM consulting services specializing in Zoho solutions and other CRMs. Customerization suggested using Zoho Analytics, an advanced Business Intelligence tool, to synchronize customer, sales, and product information from Oracle to Analytics. This “light” integration enabled SMP to avoid costly and time-consuming point-to-point API integration between the two systems.
Furthermore, Customerization embedded Analytics dashboards and reports directly into Zoho CRM and set up a customer marketing capability using Zoho’s marketing suite (Campaigns). This unified system allowed SMP’s sales team to access accurate customer data, enabling them to manage customer relationships profitably and drive more revenue, all within two months and at a fraction of the cost of an Oracle ERP extension and development.
Over to you
When it comes to choosing between ERP and CRM software, businesses need to carefully evaluate their needs and budget. If your primary goal is to optimize your business operations, then ERP may be the better choice for you. However, if you’re looking to enhance your customer experience and build lasting relationships with your clients, then CRM may be the way to go.
Ultimately, the right choice will depend on your unique business needs and goals. It’s important to thoroughly evaluate both options and choose a system that will help drive growth, efficiency, and success for your organization.
The implementation of CRM/ERP systems is a crucial process that requires meticulous planning down to the smallest details. That’s why organizations often seek the services of external consultants who can assist not only in strategy formation but also in its execution. They can identify potential challenges, suggest best practices, and ensure a smooth transition throughout the implementation process.
If you are a Canadian company, you can take advantage of the services of CDAP (Canada Digital Adoption Program) digital advisors by applying for a grant to digitalize your small or medium-sized business.
Related posts:
No related posts.
